This document defines the German abbreviations, designations and terms that are found on these Naval Gun pages. Thanks to M.J. Whitley, who provided many of these abbreviations, and to Peter Lienau and Lutz Bernhard, who provided several translations.
Bdz. - Bodenzünder - Base Fuze.
Br - Brandkörper - Incendiary.
Füllpulver or Fp - "Filling Powder." Designation for shell burster explosives.
Füllpulver C/88 - "Filling Powder C/88" where C/88 = 1888. Naval picric acid. This was used as a burster prior to the adoption of TNT.
Füllpulver C/02 or Fp 02 - "Filling Powder C/02" where C/02 = 1902. This was TNT. German shell bursters in the 1902 to 1945 period were mostly TNT mixed with beeswax as a desensitizer. The explosive mixtures were identified by code names which indicated the percentage of beeswax used in the mixture.
Fp 1 = TNT 100%
Fp 5 = TNT 95% + wax 5%
Fp 10 = TNT 90% + wax 10%
Fp 15 = TNT 85% + wax 15%
Fp 20 = TNT 80% + wax 20%
Np - Nitropenta. An explosive better known as Pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN). This was used as the burster in smaller-caliber weapons such the 3.7 cm SK C/30 and as a primer in larger caliber shells. When shown such as "Np 15" it means that the burster was a mixture that included 15% wax.
Führungsbänder - Driving Band.
Geschoss - Projectile.
Granate or Gr. - Shell.
Sprenggranate or Spgr. - Explosive shell.
Holzspitze - Wood block used in the nose of the burster cavity as a shock absorber.
Iz - Innen-Zünder. Internal Fuze.
Kappe - Armor Piercing Cap.
Kz - Kopfzünder. Nose Fuze.
Leucht geschoss or Lg. - Star shell or illumination projectile.
Leuchtspur or L'spur." - Tracer.
Patrone or Patr. - Cartridge. When used in ammunition designations, means that it is a fixed round type.
Pfeilgeschoss - Arrow Shell. A fin-stabilized HE projectile.
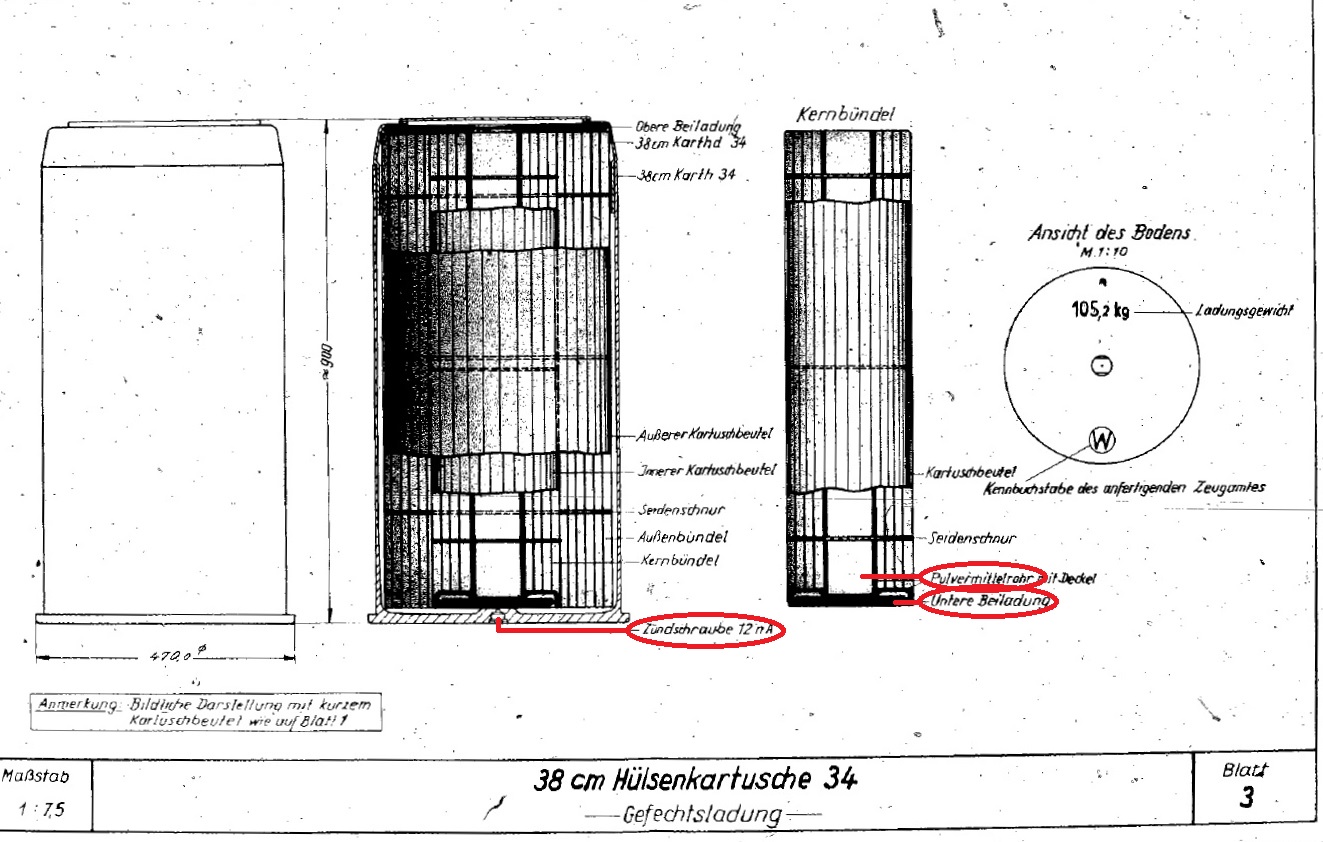
Pulvermittelrohr - Center Powder Tube - A special powder grain used in large caliber fore and rear charges. When the primer (zündschraube) in the rear charge was fired and ignited its primer charge (untere beiladung), the resulting flames ran up the center tube and ignited the rest of the propellant charge. This in turn ignited the primer charge (beiladung) in the fore charge and the resulting flames ran up its center tube and ignited its propellant charge.
Psgr. - Panzersprenggranate. Armor Piercing projectile (AP or APC).
Spgr. Bdz. or Spr.gr. Bdz. - Sprenggranate mit Bodenzünder. HE projectile with Base Fuze, can be thought of as a SAP type.
Spgr. Kz. or Spr.gr. Kz - Sprenggranate mit Kopfzünder. HE projectile with Nose Fuze.
Spgr. Bdz u. Kz or Spr.gr. Bdz u. Kz - Sprenggranate mit Bodenzünder und Kopfzünder. HE projectile with both Base and Nose Fuzes.
Stahlschrapnel - "Steel Shrapnel." Shrapnel shell using spherical steel bullets as the payload. The burster cavity was filled with pitch to hold the bullets in place.
L (as in "L/4,2") - Lange. "Length." The length of the projectile in calibers (multiples of the diameter of the projectile).
mh or mhb or m.Hb - mit Haube. "With Cap." This is used as a suffix to designate a projectile that has a windshield (ballistic cap). German APC of the World War I era had a very small windshield and the Germans did not designate these projectiles with the m.Hb suffix.
Nb.gr. - Nebelgranate. Smoke Shell.
Ad.gr. - Adolph granate. Special projectile for the 40 cm SKC/34 coastal artillery guns known as "Adolph."
Si.gr. - Siegfried granate. Special projectile for the 38 cm SKC/34 coastal artillery guns known as "Siegfried."
Sprengladung - Explosive Charge. "Burster." German bursters for Psgr. (APC) and Spgr. Bdz. (SAP) type projectiles generally used a TNT/beeswax mixture made into blocks that were pre-formed to the cavity shape. Blocks in the nose of the cavity had larger percentages of beeswax while successive blocks had lower concentrations. Blocks were wrapped in paper and were placed into cardboard containers which were labeled with the name or abbreviation of the manufacturer, a date code and the reiner Sprengstoff or "actual explosive" weight (see below). A Holzspitze (wood block) cushion was placed at the top of the cavity in some shells and felt "washers" were inserted between burster sections to lessen the impact shock and thus reduce the chances of a premature detonation. Bursters for Spgr. Kz. (HE) type projectiles were similar but generally used 100% TNT. In Kriegsmarine documents such as the "Merkbuch über die Munition" series (M.Dv.Nr. 170,xx), two weights are given for the burster, shown such as 17,568 (16,718). The first number given is for the Gesamtgewicht, the total burster weight including the explosive plus all other items such as the beeswax desensitizer and the cardboard packing material. The second number is the reiner Sprengstoff and is the actual explosive weight. When these documents are used as source material on NavWeaps, the burster weight values shown are always for the actual explosive weight. In these same documents, you will see burster notes such as Fp 1 u. 15. This means that the burster was made up of two sections, the first one made with blocks of Fp 1 (base section) and the second from blocks made with Fp 15 (nose section).
Hülsenkartusche - "Rear Charge." Most German guns of 20.3 cm (8 inches) and larger calibers had the propellant divided into two parts, the "fore charge" in a silk bag and the "rear charge" in a brass cartridge. These were usually rammed together. Brass cartridge cases were replaced by steel during the war.
Vorkartusche - "Fore Charge." This was in a double silk bag, which gave some protection from "flash." During World War I, it was common to use double brass bands to stiffen the bags, but this was abandoned prior to World War II as it was believed that metallic deposits in the bores had caused split liners.
RP - Rohr-Pulver. "Tube powder," the descriptive designation given to German gun propellants. These propellants were manufactured in the form of hollow tubes. The propellants were classified by model year and by the external and internal diameters of the tubes in millimeters. For example, propellant designated as RP C/38 (14/4.9) would be a tube powder first introduced in 1938 that had an external diameter of 14 mm (0.551 in) and an internal diameter of 4.9 mm (0.193 in). German propellants of the twentieth century were double base types made from nitrocelluose and a plasticizer. Several compositions were used from 1912 to 1945. Earlier ones used nitroglycerin as the plasticizer while later ones used diethylene glycol dinitrate, which was cooler-burning and less bore erosive. All were resistant to exploding even when exposed to a hot fire. For instance, when the small battleship Gneisenau was bombed at Kiel in 1942, she had over 24 mt (23 tons) of propellant ignited in a forward magazine. There was no explosion even though turret "Anton" was lifted at least 50 cm (20 inches) from its mounting by the gas pressure. The British did extensive studies of RP C/12 following World War I and developed "Solventless Cordite" (SC) based upon the results to replace their earlier cordite propellants.
Gu RP - Nitroguanidine propellant in hollow tubular form. It is noted in USNTME Report No. 261-45 that Nitroguanidine was also used as a burster material in Naval shells of 28 cm, 30.5 cm, 38 cm and 40.6 cm.
Shell Colors - AP shells had blue bodies, HE (both nose and base fuze types) had yellow bodies, practice shells had red bodies and Illumination shells had green bodies. A base-fuzed shell with the nose painted black indicated that the shell was fuzed. A black band around the shell indicated the balance point.
Sulfittri - Burster TNT.
Wolfram - Tungsten.
Zerl - Self destructing projectile
Panzergranate - AP projectile
bekappte Panzergranate - AP projectile with an AP Cap.
Zündergranate - SAP projectile
bekappte Zündergranate - SAP projectile with an AP Cap.
Gewicht der Sprengladung samt Umhüllung - "Weight of explosive charge including wrapping." Burster designation
equivalent to the German Gesamtgewicht (see above). Unlike the Germans, the Austro-Hungarian Navy did not
also define the Reiner Sprengstoff weight of the actual explosives. Austro-Hungarian burster weights on NavWeaps
datapages are for the Gewicht der Sprengladung samt Umhüllung weights.
C - Construktionjahr. "Year of Construction." Year that design or manufacturing started. Usually shown with a number, such as C/38 meaning that design was started in 1938. This was also spelled as Konstruktionjahr and some Krupp guns purchased by Austria-Hungary in the 19th century used a "K" instead of a "C" in the designation.
FLAK - FliegerAbwehrKanone. Literally means "Flier Defense Cannon." Designation used for AA weapons (FLAK guns). During World War I, this term was used by Allied airmen to describe the shell bursts from such weapons ("taking Flak"), which has become the current accepted meaning of the term.
FLAK M - FLAK Marine. Naval FLAK gun.
Gerät - "Equipment." Used to identify experimental weapons during World War II. Usually used together with an identifying number.
K - Kanone. "Cannon." Used by Krupp to designate their breech loading bag guns of the 1890s.
KM - Kanone Marine. "Naval Cannon." Usually followed by the year in which it was designed. For example, a gun with the designation KM42 would mean a naval gun designed in 1942. This designation system was used for some guns designed between 1940 and 1945.
L (as in "L/45") - KanoneLange. "Cannon Length." Length of the gun barrel in multiples of the bore diameter.
na - neue Art. "New Design."
nT - neue Technologie. "New Technology."
SK - Prior to 1920, this was for deck guns and meant Schnelladekanone or Schnellfeurkanone. "Fast Firing Cannon," equivalent to QF or RF. After that date, the meaning was changed to Schiffskanone or "Ship Cannon." Usually followed by the year in which it was designed. For example, a gun with the designation SK C/34 would mean that the weapon was a naval cannon designed in 1934. This designation system was used for most guns designed between 1920 and 1940.
TBK or Tbts K. - Torpedoboots Kanone. "Torpedo Boat Cannon."
UBK or Ubts K. - Untersee-Boots Kanone. "U-boat Cannon."
Range Tables - Beginning in 1906, all muzzle velocity measurements were made 25 m to 100 m (80 to 330 ft) in front of the muzzle and averaged to match a 10/30 gunwear rating (average gun). This number is used for the range table "V0" (aka, Muzzle Velocity) and is sometimes labeled as "schußtafelmäßige V0" (range table MV), indicating that this is an arbitrary value for range table purposes. New gun V0, sometimes called "größte V0" (highest MV) is approximately 103.3% of V0, but with a scatter around this value due to individual gun and charge differences. For example, the range table V0 for the 30.5cm SK L/50 gun was 855 mps (2,805 fps) with full charges. The new gun V0 would thus be 103.3% of this value, or about 880 mps (2,890 fps). The range tables were constructed with the assumption that the propellant temperature was 15°C (59°F). In addition, up until 1919 the range tables assumed that the ambient air at sea level had a density of 1.206 kg/m3 (0.0753 lb/ft3), a temperature of 15°C (59°F) and a humidity of 50%. For the 1919-1945 range tables, the ambient air at sea level was assumed to have a density of 1.245 kg/m3 (0.0777 lb/ft3), a temperature of 10°C (50°F) and 70% humidity.
BSG - Bettungschiess-Gerüst. "Platform firing framework." These were mountings for large caliber guns used as coastal artillery and resembled a railway mounting without the rail bogies. They were supported on a concrete platform by a central pivot and ball race with a roller or bogie at the rear running on a circular arc.
Lafette - Mount.
Laffetierung - Mounting.
Geschützlafette - Gunmount.
Ein - Einheitslafette. "Universal Mounting." Meant that the weapon could be used against either aircraft or surface targets - Dual Purpose.
Drehscheibenlafette - Rotating Turretmount.
Dopp MPL - Doppelt Mittel-Pivot-Lafette. "Twin central pivot mounting."
Dop L - Doppellafette. "Twin mounting."
DrhL - Drehscheiben-Lafette. "Turntable mounting." Generally used for turret mountings.
Drh Tr - Drehturm. Another abbreviation for "Turret."
Kst.Drh.L - Küsten-Drehscheiben-Lafette. "Coastal turntable (turret) mounting." A type of mounting for coastal artillery weapons.
ML - Marine-Lafette. "Naval Mounting."
MPL - Mittel-Pivot-Lafette. "Central pivot mounting."
Schiessgerät - "Firing Equipment." Description used for some coastal artillery mountings.
Turm - "Turret." Türme is the plural form.
Doppelturm - Twin turret. Doppeltürme is the plural form.
Dreifachturm - Triple turret. Dreifachtürme is the plural form.
FLAK L - FLAK-Lafette. Anti-aircraft mount.
Tbts L - Torpedoboots-Lafette. Torpedo-boat mount.
Ubts L - U-boots-Lafette. U-boat mount.
05 September 2007 - Benchmark
26 January 2009 - Added definitions for na and nT
12 January 2010 - Added definition for Ein
04 April 2011 - Added to SK definition
21 August 2011 - Added definition for Sprengladung
22 May 2012 - Updated to latest template
20 November 2012 - Added definition for K
03 February 2019 - Minor changes
23 March 2019 - Updated to latest template
30 April 2020 - Updated to HTML 5 format
06 June 2020 - Added definitions for Bdz, Kz and Führungsbänder
31 December 2022 - Added definition for Stahlschrapnel
13 May 2023 - Noted that the m.Hb suffix was not used for APC of the World War I era
15 February 2024 - Added Austro-Hungarian definitions
03 April 2024 - Added TNT burster code names and picric acid definition
29 September 2024 - Added Zerl, Np and Iz definitions and added to Sprengladung and RP definitions
09 November 2024 - Added to Sprengladung definition
07 January 2025 - Corrected typographical error
02 February 2025 - Added Range Tables definition
18 April 2025 - Added definition for Pulvermittelrohr and Nitroguanidine